|
Tokyo, September 26, 2001 -- Hitachi, Ltd. (TSE: 6501) today announced
the world's first single-chip STN color liquid crystal display controller
driver “HD66766” that handles 65,536 colors as liquid crystal
display for mobile communication terminals such as digital portable
telephones and the largest screen in the industry, 132 × 176
pixels. Hitachi will start sample shipment on October 1, 2001 in Japan.
This product enables display of various colors and high-quality pictures
without irregularities, enabling real display such as photographic
images. A combined use of multi-color software enables display of
260K colors.
Recently, the roles of digital mobile phones have been increasing
rapidly as data communication terminals in information distribution
services such as electronic mail and Internet contents. In addition,
display information has become more diverse such as photo images created
by installing a portable camera, as well as text and graphic information.
As a result, introduction of a large screen for handling display of
continuously increasing information and multi-color feature for more
realistic display is advancing for the liquid crystal display panel
that is installed in mobile phones. There is strong demand for a liquid
crystal control driver that handles these features.
Hitachi has developed a single-chip “HD66761 (256 colors, 128
× 80 pixels)” and chip sets “HD66765 and HD66764 (4,096
colors, 132 × 176 pixels)” as controller drivers for STN
color liquid crystal display for mobile communication terminals. This
time, Hitachi developed a single-chip controller driver for STN color
liquid crystal display “HD66766” for 65,536 colors first
in the world by 48V high voltage and fine process to respond to the
strong demand from the market for further increase of colors, a large
screen, and compact mounting.
The HD66766 enables display of 65,536 colors and a large screen of
132 × 176 pixels. As a result, photographic images created by
cameras can be displayed more realistically. By combining with multi-color
software through dither processing *1,
260K colors can be displayed. In the conventional 4,096-color display,
one pixel data consists of 12 bits. This product incorporates large
capacity RAM of 372K bits and data of one pixel consists of 16 bits.
Since the CPU processes 2-byte data in the same way, display of 65,536
colors can be achieved without increasing the CPU load.
An increase of screen size or introduction of color display not only
requires a higher liquid crystal driving voltage, but also means a
deterioration of the quality of images displayed and an increase of
current consumption. Since the general method of applying a conventional
liquid crystal driving voltage drives segment signals and common signals
within the same voltage range, the current consumption of liquid crystal
display devices increases as the liquid crystal driving voltage increases.
However, since this product uses a Hi-FAS liquid crystal driving *2
method that can drive segment signals operating at high speed with
a low voltage, it requires 30% to 40% less current consumption for
liquid crystal display devices in comparison to the existing method.
Improvement of response performance of a liquid crystal panel for
displaying animation causes flickers due to the absence of afterimages
on the liquid crystal panel in the frame thinning gradation *3,
causing deterioration of picture quality. This product applies a pulse-width
gradation method *4, which does
not depend on afterimages to display images without flickers, achieving
high-quality images.
A COG *5 installation method that
connects a controller by directly facing down on a LCD glass substrate
is applied. Common drivers are assigned on both ends of the segment
driver area as pin assignment within LSI, achieving center assignment
where wiring on both ends of the LCD display unit is well balanced,
thereby enabling compact installation.
Hitachi will continuously improve the lineup by developing products
corresponding to various display screen sizes.
| Notes: 1. |
Dither processing: Processing that increases the
number of colors by controlling generation of half tones through
the picture element layout pattern on liquid crystal display |
| 2. |
Hi-FAS (Hi-Frequency Amplitude Selection) driving:
Method that drives signals in different voltage ranges by increasing
the driving voltage of common signals that operate at a low speed
and reducing the driving voltage of segment signals that operate
at a high speed. As a result, a voltage difference between segment
signals and common signals can be secured for actual liquid crystal
display. Although the circuit structure becomes more complicated,
current consumption of a liquid crystal display unit can be reduced. |
| 3. |
Frame thinning gradation method: Method that achieves
half tones by using afterimages of liquid crystal through ON/OFF
control according to the gradation data for each frame |
| 4. |
Pulse width gradation method: Method that achieves
half tones by adding ON/OFF waveforms to the liquid crystal panel
only for a period matching the gradation data for each line. Since
the ON/OFF time interval is short, this method can achieve picture
quality with less flicker than that of frame thinning gradation
method. |
| 5. |
COG (Chip On Glass): Method that installs a chip
with a gold bump by directly facing down on a LCD glass substrate |
< Typical Applications >
 |
Mobile phones that handle electronic
mail and WWW contents services |
 |
Mobile phones that handle high-speed
data transfer (W-CDWA, GSM, etc.) |
 |
Portable PDA, handy GSP terminal,
and handy POS |
 |
Portable digital audio player |
< Prices in Japan > (For Reference)
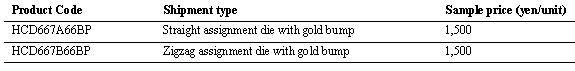
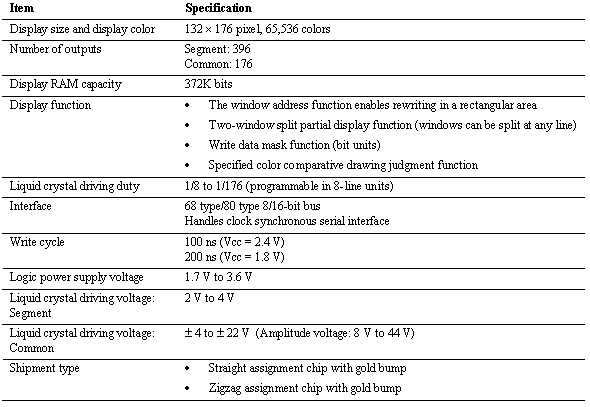
< Specifications >
 |