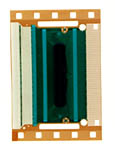
“HD66336” 64-grayscale TFT LCD driver
incorporating RSDS-compliant interface
Tokyo, October 25, 2001— Hitachi, Ltd. (TSE: 6501) today announced
the 64-grayscale HD66336 TFT LCD driver incorporating an RSDSTM*1-compliant
interface offering low EMI*2 , as a data line
driver for XGA*3, and SXGA*4
size high-definition TFT LCD panels. Sample shipments will begin in
November 2001 in Japan.
TFT LCD panels mounted in monitors, space-saving desktop PCs, and
notebook PCs, are becoming available in larger screen sizes and with
higher definition. With the increasing volumes of screen display information
that this involves, there is a trend toward higher speeds on the interface
between the CPU and LCD driver. However, since the data interface
frequency is higher than that for LCD drive signal output, higher
speeds mean increased effects of EMI noise caused by changes in signal
level. Suppression of EMI noise is therefore a major concern in LCD
panel system design, and there is strong demand for LCD drivers that
enable EMI noise to be reduced.
In response to this need, Hitachi has been engaged in the development
of TFT LCD drivers for data line drive incorporating an RSDSTM-compliant
small amplitude differential interface that enables a low EMI level
to be achieved. The initial product developed was the 384/420-output
HD66335 for XGA and SXGA+*5, and the lineup
has now been enhanced with the development of the dedicated 384-output
HD66336, designed for lower cost, for XGA and SXGA applications.
The HD66336 employs an RSDSTM-compliant small
amplitude differential interface. The voltage amplitude has been reduced
to 0.4 V (±0.2 V) compared with the approximately 3 V of a conventional
CMOS level interface, enabling EMI noise due to signal level changes
to be decreased and also making it possible to reduce the number of
parts necessary for noise suppression, such as shielding components
and capacitors. Moreover, the number of data interface lines has been
halved to 18 from the 36 lines of a CMOS level interface, enabling
the board wiring area to be reduced and LCD panel costs to be cut.
The HD66336 is a data line driver suitable for use with XGA and SXGA
high-definition color TFT LCDs. It receives 6-bit digital data per
pixel and generates voltages for 64-grayscale by means of D/A converters,
providing 260,000-color display. With 384 data line drive outputs,
XGA display can be handled by eight chips and SXGA by ten, allowing
efficient LCD panel design that uses all the pins.
The HD66336 is available in a COF*6 or TCP*7
package.
Future plans call for further extension of the lineup of TFT LCD drivers
incorporating an RSDSTM-compliant interface,
including the development of products supporting 256-grayscale and
the larger-screen UXGA*8 standard.
| Notes: |
1. |
RSDSTM (Reduced
Swing Differential Signaling): An interface technology. RSDS is
a small amplitude differential interface technology proposed by
National Semiconductor Corporation of the U.S.A., and its trademark.
|
| |
2. |
EMI (Electro Magnetic Interference):
Generic term for emission phenomena including electromagnetic
interference emitted outside of an electronic device.
|
| |
3. |
XGA (Extended Graphics Array): A display
definition standard. XGA is a trademark of IBM Corporation, indicating
a display comprising 1,024 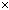 768 dots.
768 dots.
|
| |
4. |
SXGA (Super Extended Graphics Array):
A display definition standard. The display comprises 1,280 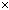 1,024 dots.
1,024 dots.
|
| |
5. |
SXGA+ (Super Extended Graphics Array
plus): A display definition standard. The display comprises 1,400
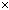 1,050 dots. 1,050 dots.
|
| |
6. |
COF (Chip On Film): A package mounted
on an ultra- thin-film tape allowing bending of 1 mm or less,
.
|
| |
7. |
TCP (Tape Carrier Package): A package
mounted on a thin-film tape, allowing ultra-thin type mounting
(1 mm or less).
|
| |
8. |
8. UXGA (Ultra Extended Graphics Array):
A display definition standard. The display comprises 1,600  1,200 dots.
1,200 dots. |
< Typical Applications >
TFT LCD panels (notebook PCs, space-saving desktop PCs, monitors)
< Prices in Japan >(For Reference)

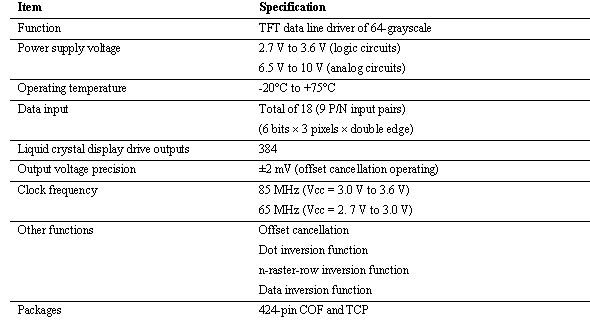
< Specifications >
|