![]()
Last Updated: April 13, 2016
Ransomware is a type of malware that infects computer systems, restricting users' access to the infected systems such as the user's systems have been locked or the user's files have been encrypted. Ransomware variants have grown very rapidly since 2015 and often attempt to extort money from victims. HIRT-PUB16001 is an advisory to address issue for Ransomware and Recent Variants.
There are two types of ransomware such as Crypto and Locker ransomware. Crypto ransomware encrypts personal files/folders (e.g., the contents of your documents, spreadsheets, pictures, videos and etc.). Locker ransomware locks the screen and demands payment. No personal files are encrypted.
The first known ransomware was the 1989 "AIDS" trojan (also known as "PC Cyborg"). It's use of symmetric cryptography.
In 2006, GPcode, Archives and etc. has been active in the wild. These crypto ransomware were use of RSA public key cryptography. Also the first known locker ransomware was the 2010 "Winlock" trojan. It locks the Windows' screen and demands payment.
Ransomware attacks re-organized around a new type of extortion by Cryptolocker. Gameover Zeus, which first emerged around September 2011, operates silently on victim computers to funnel stolen banking credentials back to the attackers. The Gameover Zeus network was as a common distribution mechanism for Cryptolocker. Also Cryptolocker began appearing about September 2013 and continued to grow rapidly.
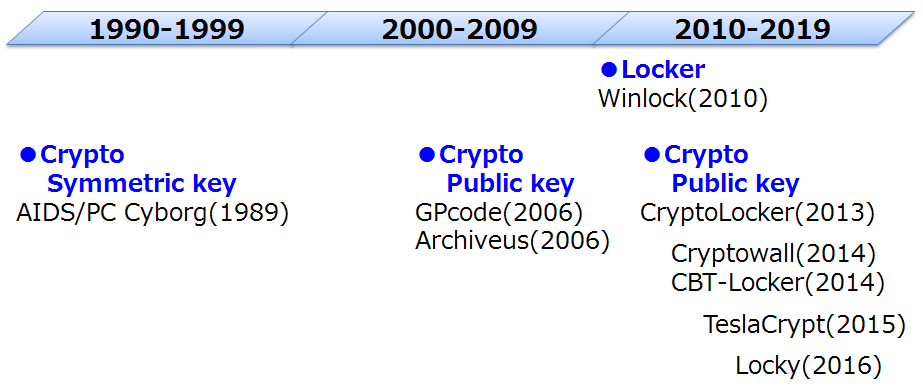
Figure 1: Brief History of Ransomware
Ransomware variants have grown very rapidly as one of various cyber attacks.
Ransomware attacks grew 113 percent in 2014. Crypto-ransomare was seen 45 times more frequently. (Symantec, 2015 Internet Security Threat Report, Volume 20 (Apr. 2015))
In 2015, 64 percent of binary-file-based ransomware detected have been crypto ransomware while binary-based locker ransomware made up the remaining 36 percent. For crypto ransomware, Japan comes in at number two whereas for locker ransomware, it occupies the sixth spot. (Symantec, The evolution of ransomware (Aug. 2015))
The total number of ransomware samples grew 127% in the past year. Ransomware continues to grow very rapidly - with the number of new ransomware samples rising 58% in Q2. (McAfee Labs, Threats Report (Aug. 2015))
Although a few families - including CryptoWall 3, CTB-Locker, and CryptoLocker - dominate the current ransomware landscape, we predict that new variants of these families and new families will surface with new stealth functionalities. (McAfee Labs, 2016 Threats Predictions (Nov. 2015))
Ransomware programs were detected on 753,684 computers of unique users; 179,209 computers were targeted by encryption ransomware. (Kaspersky, Overall statistics for 2015 (Dec. 2015))
|
|
Users and administrators take the following preventive measures to protect your computer networks from ransomware infection.
Restore or decrypt encrypted files by ransomware
+ Perform and test regular backups to limit the impact of data or system loss.
+ Data should be kept on a separate device, and backups should be stored offline.
Protect your file from ransomware encryption
+ Restrict users' permissions to run untrusted applications, and apply the principle of "Least Privilege" to all systems and services.
Protect your system from ransomware infection
+ Keep your operating system and software up-to-date with the latest patches.
+ Maintain up-to-date anti-virus software, and scan all software downloaded from the internet prior to executing.
| YearMonth | Ransomware Name |
| Mar. 2016 | KeRanger References: Symantec: KeRanger: First Mac OS X ransomware emerges (Mar. 2016) |
| YearMonth | Ransomware Name |
| May. 2014 | ANDROIDOS_LOCKER.HBT References: Trend Micro: Android Ransomware Uses TOR (Jun. 2014) |
| YearMonth | Ransomware Name |
| Nov. 2015 | Linux.Encoder Decryption tool: Decrypter References: Dr.WEB: Linux.Encoder.1 (Nov. 2015) Ransomware Found Targeting Linux Servers and Coding Repositories (Nov. 2015) |
Masato Terada (HIRT) and Naoko Ohnishi (HIRT)