![]()
Last Update: October 10, 2017
Beginning from June 27, 2017, the ransomware NotPetya (also known as Petrwrap, GoldenEye and Nyetya) has been active in the wild.
Ransom activities
NotPetya encrypts the MBR (Master Boot Record) of infected Windows computers, making affected machines unusable. In addition, it displays a ransom note like the one in Figure 1.
Diffusion activities
NotPetya attempts to propagate itself. In the process of propagating itself, this malware spreads by exploiting a vulnerability in Windows SMBv1 (vulnerability CVE-2017-0145, addressed by security update MS17-010) and by stealing the user's Windows credentials.
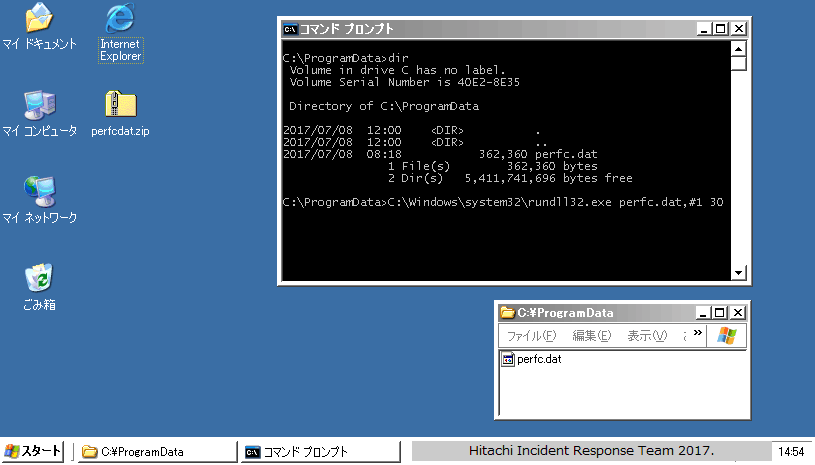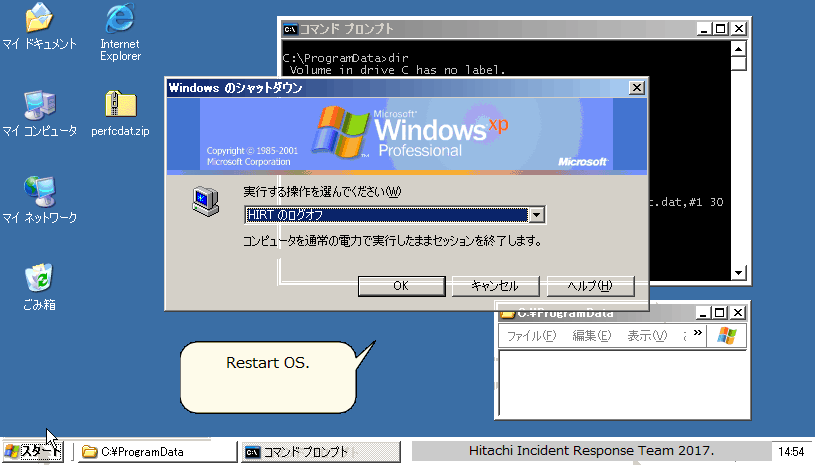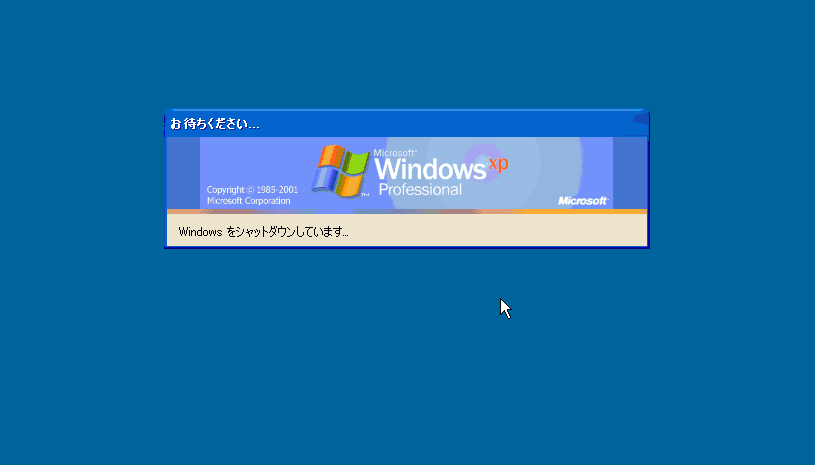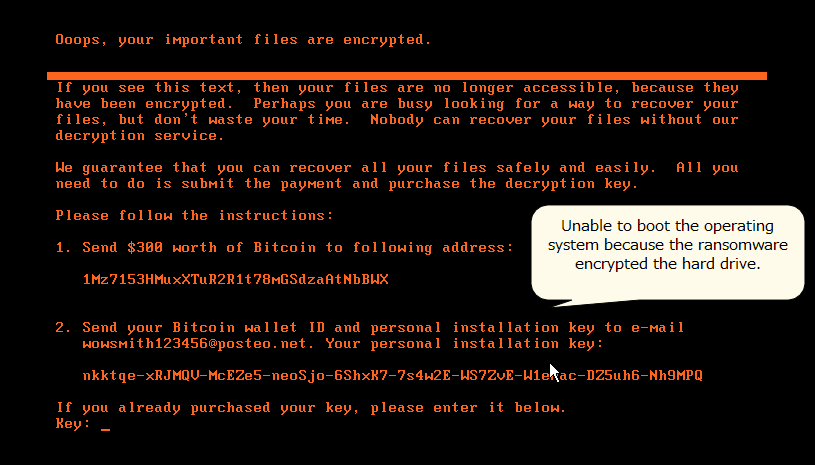
Figure 1: Ransom note
June 27, 2017
Various organizations have issued the following security alerts.
Hitachi products using Microsoft Windows operating systems are affected to this issue.
HIRT recommends that the following measures are effective in your network environment such as information systems, healthcare systems, industrial control systems and etc. to prevent Ransomware NotPetya.
Notpetya
SHA256:027cc450ef5f8c5f653329641ec1fed91f694e0d229928963b30f6b0d7d3a745
MD5:71b6a493388e7d0b40c83ce903bc6b04
NotPetya(SHA256: 027cc450ef5f8c5f653329641ec1fed91f694e0d229928963b30f6b0d7d3a745) was executed on an infected PC in the experimental network environment. The following presents the results of an investigation into the probe method of new PCs for infection as characteristic of a network worm.
NotPetya on the infected PC uses the known IP address such as "All computers in the ARP cache", "All computers you have a current open network connection with" and etc. to access port 445/tcp, 139/tcp and 80/tcp on other PCs. For more information, please refer to the Symantec report.
Figure 2 shows that NotPetya accesses a default gateway which provides Web administration interface on port 80/tcp. This is an example using IP addresses of "All computers in the ARP cache".
Figure 3 shows that NotPetya accesses PC which has connected with port 22/tcp of a current open network connection and in outside of subnetwork. This is an example using IP addresses of "All computers you have a current open network connection with".
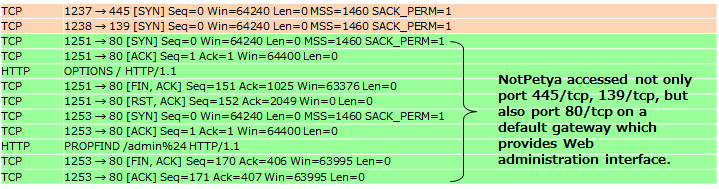
Figure 2: An example using IP addresses of "All computers in the ARP cache"
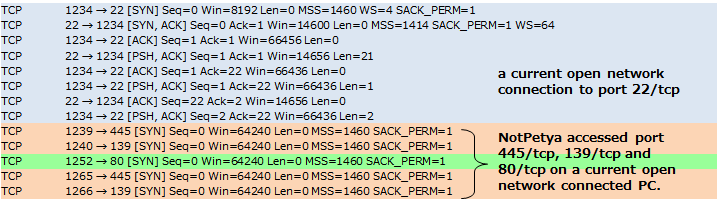
Figure 3: An example using IP addresses of "All computers you have a current open network connection with"
Also NotPetya on the infected PC uses ARP packets to probe other operating PCs in the same network.
The following figure, Figure 4, shows the elapsed time of probing the same subnetwork (/24: about 250 IP addresses) by NotPetya and WannaCry. WannaCry is to about 30 secondes. The probing performance of NotPetya (about 15 minutes) is not particularly high, and it is that NotPetya operates with the assumption that its activities will access the known IP address over an intranet and the Internet, as a result to increase the speed of its diffusion.
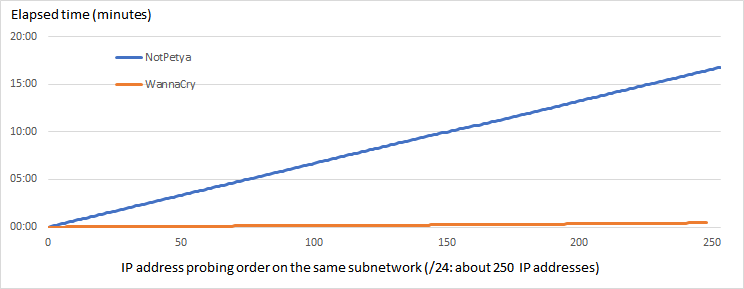
Figure 4: Elapsed time of probing IP address order on the same subnetwork (/24: about 250 IP addresses).
Masato Terada (HIRT) and Naoko Ohnishi (HIRT)