Symbiotic Evolution Architecture
that realizes mission critical IoT
to advance DX
Due to phenomena such as climate change and pandemics in addition to the changes in the business environment brought about by progress in digitalization, social uncertainty is steadily increasing.
Until now, social infrastructure has sought things such as stable operation, increased efficiency, and improved convenience.
Information control systems have also evolved as systems that fulfill those requirements.
From now on, in addition to these requirements, it is necessary to build the so-called dynamic capability in order to respond to the surrounding uncertainty.
Dynamic capability# refers to:
Sensing: The capability to sense threats and dangers
Seizing: The capability to seize opportunities and reconfigure existing assets, knowledge, and technologies to gain competitiveness
Transforming: The capability to revamp and transform organizations overall in order to make competitiveness sustainable
Therefore, dynamic capability is a capability that should be possessed in order for companies to survive in an age of increasing uncertainty.
As examples of the uncertainty surrounding social infrastructure, in the electricity field there is a rapid change in the composition of energy sources aimed at decarbonization, in the railway field there are widespread changes in demand due to COVID-19, and in the field of industry there is increasing delivery risk due to interruptions in the supply chain.
Hitachi believes that realizing mission critical IoT is the key to realizing social infrastructure that can flexibly respond to changes while guaranteeing stable operation.
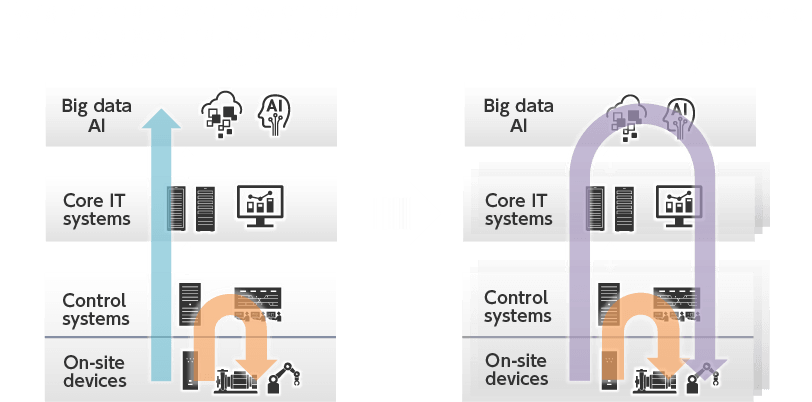
Traditional information control systems have utilized on-site data and data from core IT systems to improve and optimize the efficiency of operations, but it was difficult for the control systems that control machines on site to directly apply the results of data analysis.
From now on, in order to sense and seize various changes and build systems that will flexibly respond to these changes, we need mission critical IoT that shares various kinds of data from sites and core IT between systems, analyzes the collected big data by using AI or other tools, and feeds back the optimization solutions gained through this process to control systems in real time.
Not only is cybersecurity important for this, but in addition to the effectiveness and credibility of cloud and other infrastructure processing and AI models for such processing, the verification and maintenance of the effectiveness and credibility of processing and telecommunication channels involved from the generation of input data for cloud processing until the data from the results of processing reaches sites are also important.
For example, it is required to enable the online attachment and addition of individual context information of telecommunications data, to allow the transmission of this information to processing on the user side, and to transmit required information, such as whether processing between nodes is being performed correctly, transmission time, content of additional processing, and AI model information used in processing, etc., to nodes on the user side.
What systems are the kind of information control systems for realizing mission critical IoT?
Here are some videos demonstrating the appearance of systems that respond to the constantly changing external environment and on-site conditions.
Based on the concept of information control systems for realizing mission critical IoT, Hitachi has compiled new architecture.
Until now, the platforms that support social infrastructure had different requirements for each layer, from control at the bottom up to core IT and cloud. These platforms had individual architectures defined and were developed accordingly.
With the aim of realizing mission critical IoT, vertically connecting the platforms in each layer is becoming very important in order to implement trust, open & seamless operation, and evolution from now on.
For example, this includes: 1) security between the edge and the cloud in order to secure the credibility of data between layers even in a zero-trust environment, 2) virtualized data fields for understanding and utilizing various kinds of on-site data on the cloud side, and 3) control orchestration of the links from the cloud to the edge to realize functional changes online.
Furthermore, horizontal connection also becomes important to link and leave systems with different subjects and purposes and flexibly evolve systems in response to environmental changes.
In this way, by coordinating the system overall from edge to cloud, it is possible to realize sensing, seizing, and transforming in social infrastructure systems.
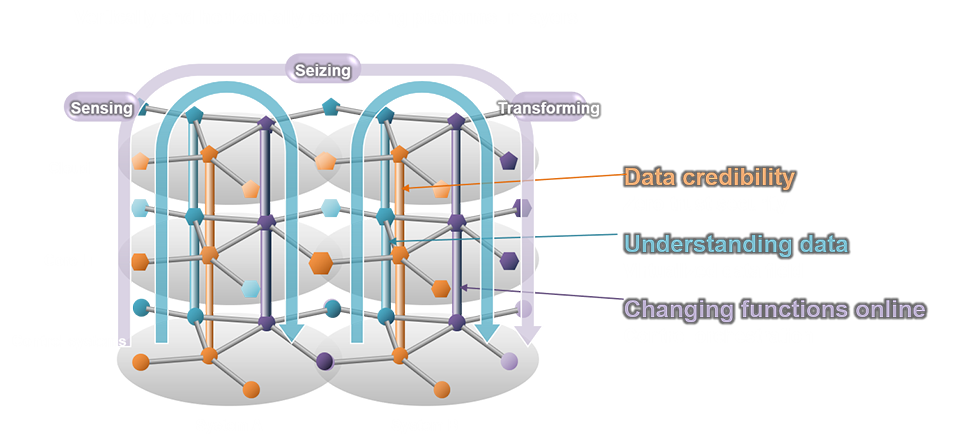
Hitachi believes the following technologies are particularly important in order to build systems depending on Symbiotic Evolution Architecture that realizes mission critical IoT.
Ensuring the durability of the entire system from control systems to the cloud environment for big data and AI, as well as the credibility and real-time nature of data being processed on the system. The following three points are important as technological elements:
Connecting sites and the cloud by using networks and 5G and understanding, distributing, and utilizing data between different layers and systems in order to link between different systems.
Being able to change the functions of control systems online in accordance with the increased performance of the edges that make up control systems, big data analysis, and the results of AI is required in order to create systems that can respond by themselves. This is enabled by realizing flexibility of system configuration elements.
![[1. Trust] Durability of system configuration elements: ① Redundant system technology; Credibility and real-time nature of data: ② High reliability and real-time, ③ DX security. [2. Open & seamless] Understanding data between the cloud and sites: ① Abstracted data interface; Utilizing cloud data on site: ② Online addable contexts; Distributing data between different systems: ③ Flat and transparent data linkage. [3. Evolution] Analyzing big data and incorporating AI, Changing functions online: ① Orchestration; Flexibility of system configuration elements: ② Data field.](/products/it/control_sys/architecture/image/img_architecture03.png)