Our method outperformed conventional methods on overlapping speech
February 3, 2020
Hitachi, Ltd. today announced the development of end-to-end*1 speaker diarization*2 method that detects speech segments (start and end times) of multiple speakers accurately by using a neural network trained with speaker-overlapping speech. Different from most of the other speaker diarization methods, which cannot handle overlapping speech, this method improves the speech recognition accuracy of overlapping speech in natural conversation. Evaluation results on a telephone speech dataset show that the method outperforms conventional methods. The technique also achieved excellent diarization error rates*3 on heavily-overlapping simulation speech datasets. Hitachi will aim to tackle the labor shortage and to contribute to the productivity improvement through applying the method to speech recognition and dialogue services.
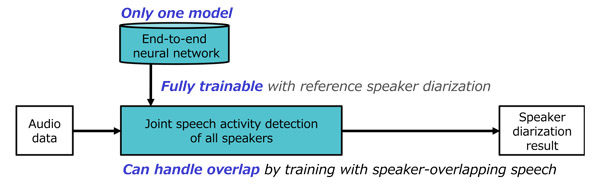
Fig. 1 Developed end-to-end speaker diarization
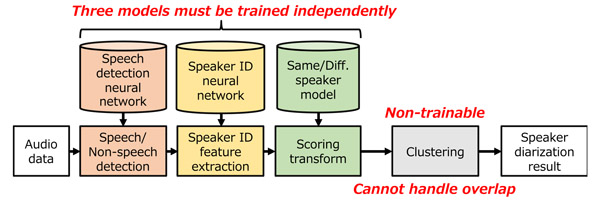
Fig. 2 Conventional speaker diarization
For more information, use the enquiry form below to contact the Research & Development Group, Hitachi, Ltd. Please make sure to include the title of the article.